|
** 아쿠아포닉의 기본원리 아쿠아포닉스(Aquaponics)는 지속 가능한 식량생산을 위한 다계층 시스템을 말한다. 즉, 수경재배(hydroponics)와 고기양식(recirculating aquaculture)을 결합한 바이오 통합 시스템이다. Aquaponics는 다음과 같은 몇 가지 기본 원칙에 따라 생태 식품 생산의 모델로 사용됩니다. 즉, Aquaponics는 토양(흙,土)을 사용하지 않고 식량을 재배하는 방법입니다. 대신 물을 이용하여 식물을 재배 합니다.그것은 물 재배(hydro-culture)의 한 유형입니다. Hydroponics(수경재배)는 물재배(Hydro-culture)의 다른 유형 입니다. Aquaponics는 전체 aquaponics 시스템의 일부로 수경 재배(Hydroponics)를 사용합니다. 그리고 또한 Aquaponics는 또한 고기 양식 (recirculating aquaculture)시스템을 사용합니다. 어떤 사람들은 수경 재배(Hydroponics)를 생선이나 유기농 물 재배(hydro-culture)를 사용하는 것이 아쿠아포닉스(Aquaponics)라고 합니다. 1.한 생물학적 시스템의 폐기물은 미생물 활동에 의해 촉진되는 두 번째 생물학적 시스템의 영양소 역할을합니다. 2. 식물과 식물의 통합은 다양성을 증가시키고 여러 제품을 생산하는 다 영양 다 배양을 초래합니다. 3. 물은 생물학적 여과 및 재순환을 통해 재사용됩니다. 4. 지역식량(local food) 생산은 건강한 음식에 대한 접근성을 제공하고 지역 경제를 향상시킵니다.
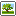
이러한 아쿠아포닉은 한마디로 자연 생태계(natural ecosystem) 라고 할수있다. 고기를 담은 수조와 식물을 재배하는 화단을 연결한 시스템에서 질소순환(nirogen cycle) 이라는 소우주(小宇宙)가 형성되어 지속적으로 식물에게는 영양소를 공급하고, 고기에게는 깨끗한 물을 공급해주는 것입니다. 아래그림과 같이 질소순환을 자연적으로, 수경재배와 같이 인공적이 아닌, 자연 생태계가 형성됩니다.
** Basic principles of Aquaponics Some people refer to the use of hydroponics as fish or organic hydroculture as Aquaponics. 1.Waste in one biological system serves as a nutrient for a second biological system, which is facilitated by microbial activity. 2. Plant-to-plant integration increases diversity and results in multinutrient multicultures that produce multiple products. 3. Water is reused through biological filtration and recycling. 4. Local food production provides access to healthy food and improves local economies. In a word, such aquaponic can be called a natural ecosystem. A microcosm called the nitrogen cycle is formed in the system that connects the fish tank and the flower bed where plants are grown, which continuously supplies nutrients to plants and clean water to fish. As shown in the figure below, the nitrogen cycle is formed naturally, not artificial, like hydroponic cultivation.
*참고자료: 질소순환도(Nitrogen circulation diagram) http://aquaponic.dothome.co.kr/aqa/board.php?board=manual&command=body&no=44
위그림과 같이 아쿠아포닉 시스템은 하나의 생태계를 형성하게되며, 시스템이 온전하게 돌아가고 있다는것은 이러한 질소순환이 자연스럽게 이루어 지고 있다는 현상이며, 아쿠아포닉 시스템의 고기와 식물이 모두 건강하다는 것이다. 세부적으로 질소순환을 이루어주는 박테리아와 물관리 분야는 다음 칼럼에서 이야기 하기로 합니다.
As shown in the picture above, the Aquaponic system forms an ecosystem, and the fact that the system is working intact is a phenomenon that this nitrogen cycle is naturally occurring, and that both fish and plants of the Aquaponic system are healthy. In the next column, we will discuss the bacteria and water management areas that make up the nitrogen cycle in detail.
|







| 

|


 aqua special
aqua special